
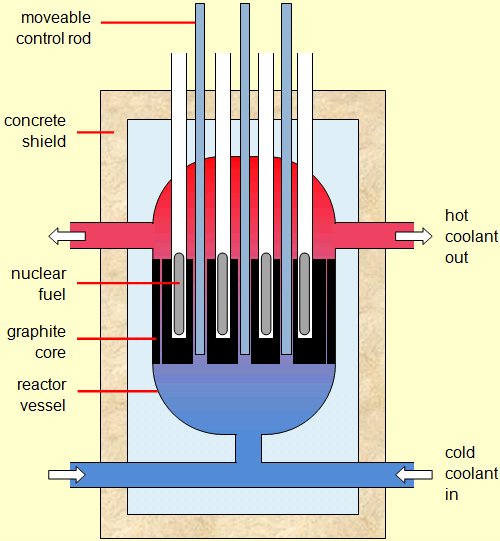
This is why fusion is still in the research and development phase – and fission is already making electricity. Key Facts Perhaps the most notable nuclear reactions are the nuclear fusion reactions of light elements that power the energy production of stars and the Sun. An uncontrolled fission reaction is the basis of an atomic bomb. The reasons that have made fusion so difficult to achieve to date are the same ones that make it safe: it is a finely balanced reaction which is very sensitive to the conditions – the reaction will die if the plasma is too cold or too hot, or if there is too much fuel or not enough, or too many contaminants, or if the magnetic fields are not set up just right to control the turbulence of the hot plasma. Many of the features of the reactor are designed to control the speed of the reaction and the temperature inside the shielding. Unlike nuclear fission, the nuclear fusion reaction in a tokamak is an inherently safe reaction. In conventional nuclear power stations today, there are systems in place to moderate the chain reactions to prevent accident scenarios and stringent security measures to deal with proliferation issues. (Updated August 2021) Fast neutron reactors (FNRs) are a technological step beyond conventional power reactors, but are poised to become mainstream. This chain reaction is the key to fission reactions, but it can lead to a runaway process resulting in nuclear accidents. The result of the instability is the nucleus breaking up, in any one of many different ways, and producing more neutrons, which in turn hit more uranium atoms and make them unstable and so on. It is triggered by uranium absorbing a neutron, which renders the nucleus unstable. Fission and chain reactionsįission is the nuclear process that is currently run in nuclear power plants. Andrea Galindo, IAEA Office of Public Information and Communication Nuclear energy is a form of energy released from the nucleus, the core of atoms, made up of protons and neutrons. The water acts as a heat transfer medium to cool down the reactor and to slow down neutron particles. nuclear fission is controlled by a medium such as water in the nuclear reactor. This chain reaction is the basis of nuclear weapons. Both reactions release energy which, in a power plant, would be used to boil water to drive a steam generator, thus producing electricity. The unique feature of nuclear fission reactions is that they can be harnessed and used in chain reactions. However, fusion is combining light atoms, for example two hydrogen isotopes, deuterium and tritium, to form the heavier helium. In fission, energy is gained by splitting heavy atoms, for example uranium, into smaller atoms such as iodine, caesium, strontium, xenon and barium, to name just a few.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
